cd /etc/yum.repos.d/ cp -f CentOS-Base.repo CentOS-Base.repo.bak rm -rf CentOS-Base.repo curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo yum clean all yum makecache
yum install rpcbind nfs-utils -y
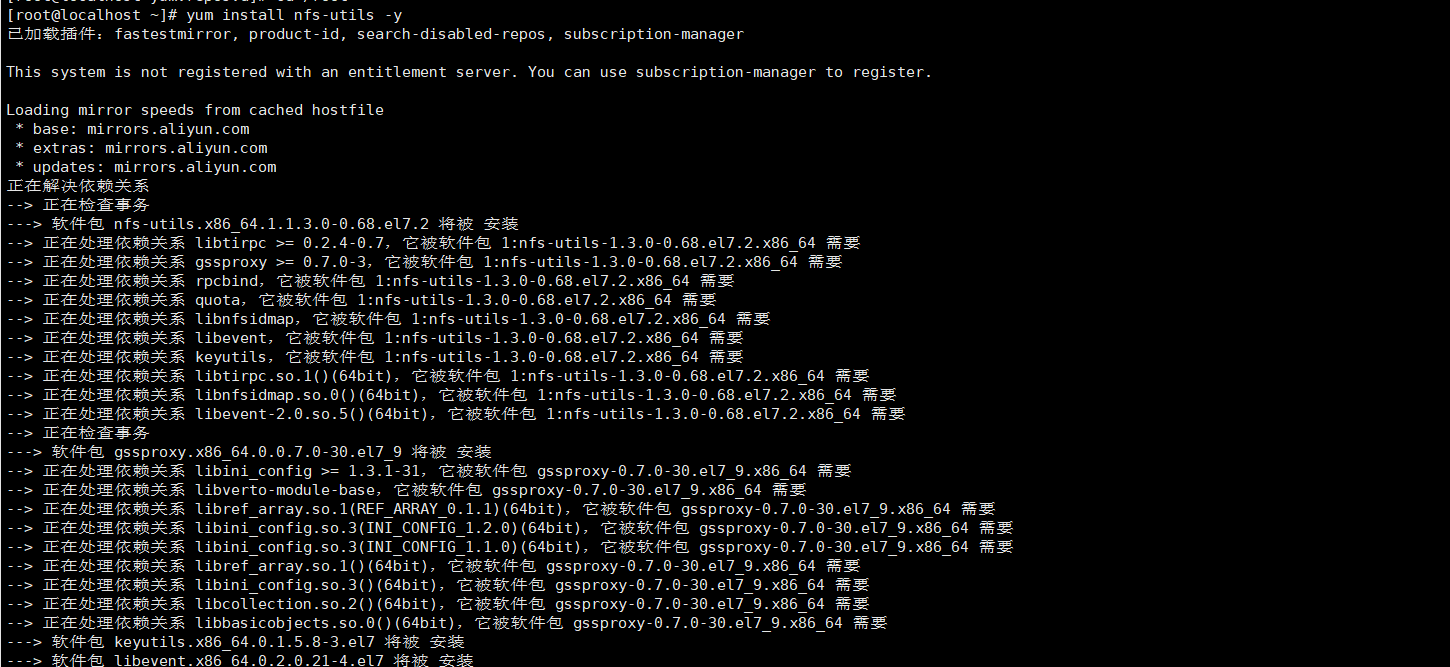
service nfs-server stop service nfs-server start service nfs-server restart # 开机启动 systemctl enable nfs-server systemctl enable rpcbind
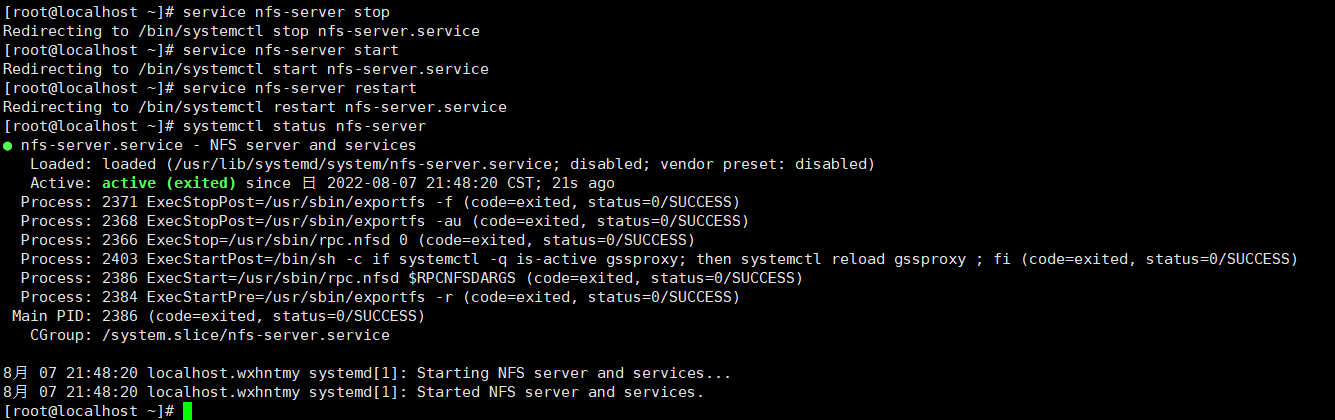
ps aux|grep nfs
NFS启动时会随机启动多个端口并向RPC注册。
为了设置安全组以及防火墙规则,此时就需要设置NFS固定端口。
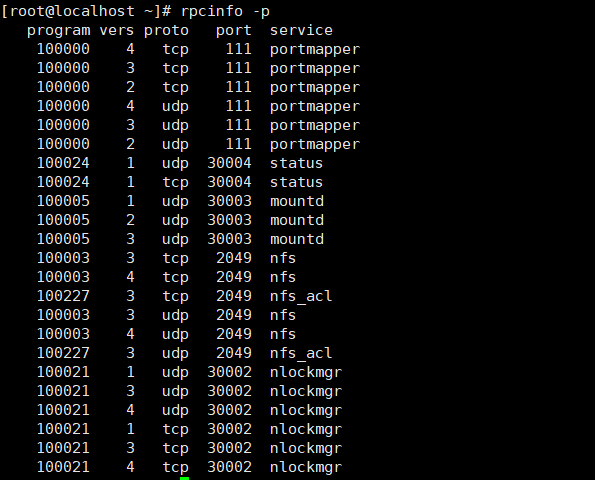
NFS服务需要开启 mountd,nfs,nlockmgr,portmapper,rquotad这5个服务.
其中nfs、portmapper的端口是固定的.
另外三个服务的端口是随机分配的.
所以需要给mountd,nlockmgr,rquotad设置固定的端口。
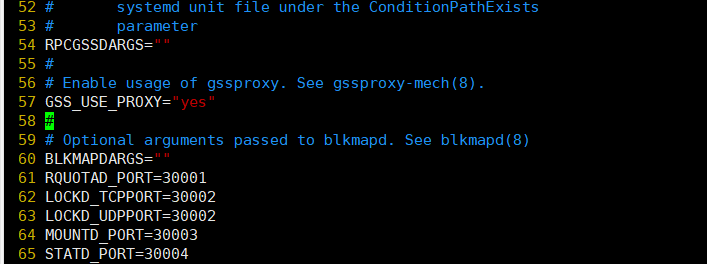
cat >> /etc/sysconfig/nfs << EOF RQUOTAD_PORT=30001 LOCKD_TCPPORT=30002 LOCKD_UDPPORT=30002 MOUNTD_PORT=30003 STATD_PORT=30004 EOF
systemctl restart rpcbind.service systemctl restart nfs.service
cat >> /etc/modprobe.d/lockd.conf << EOF options lockd nlm_tcpport=30002 options lockd nlm_udpport=30002 EOF
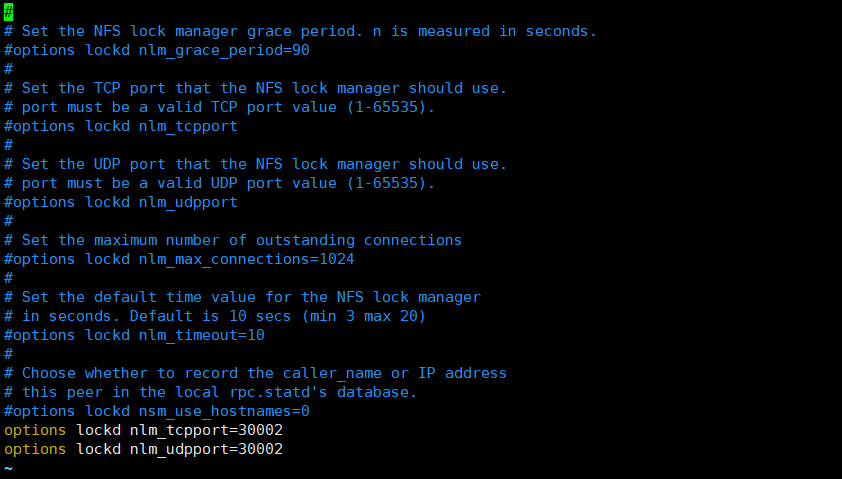
systemctl restart nfs-config systemctl restart nfs-idmap systemctl restart nfs-lock systemctl restart nfs-server
rpcinfo -p
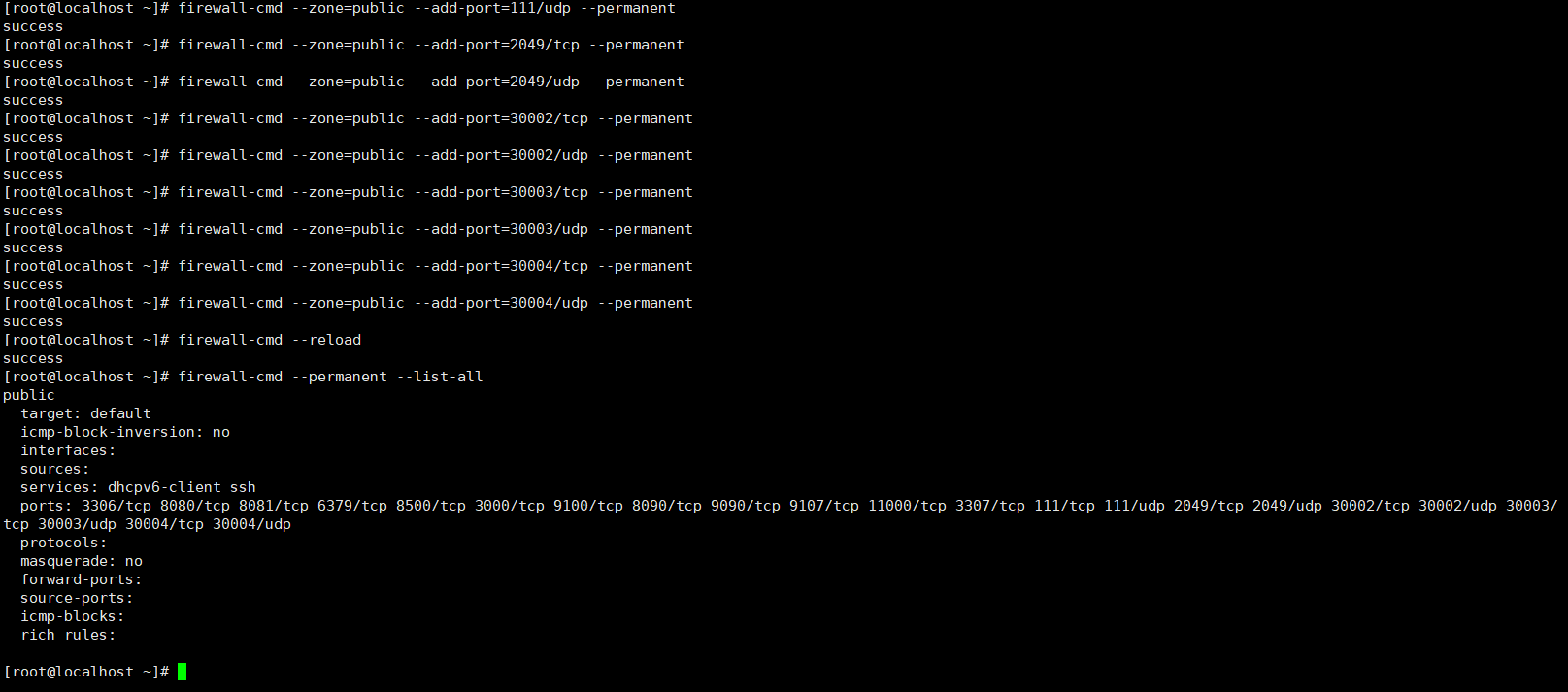
--permanent 表示永久生效,不加该参数重启后失效
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=111/tcp --permanent firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=111/udp --permanent firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=2049/tcp --permanent firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=2049/udp --permanent firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=30002/tcp --permanent firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=30002/udp --permanent firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=30003/tcp --permanent firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=30003/udp --permanent firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=30004/tcp --permanent firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=30004/udp --permanent firewall-cmd --reload firewall-cmd --permanent --list-all
mkdir /data mkdir /data/nfs vim /etc/exports cat /etc/exports service nfs-server restart
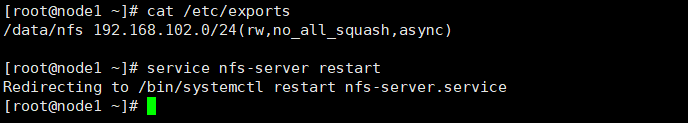
/data/nfs 192.168.102.0/24(rw,no_root_squash,async) #/data/nfs 是共享文件夹的路径,使用绝对路径,需要新建 #192.168.102.0/24 表示允许过来访问的客户机的ip地址网段,*表示不限制ip #(ro,all_squash,async)表示权限的限制 #ro 表示只读 #rw 表示可读可写 #all_squash:访客时一律被映射为匿名用户(nfsnobody) #no_all_squash:访客被映射为服务器上相同uid的用户,因此在客户端应建立与服务端uid一致的用户,否则也映射为nfsnobody。root除外,因为root_suqash为默认选项,除非指定了no_root_squash #root_squash:访客以root用户访问NFS服务端时,被映射为nfsnobody用户 #no_root_squash:访客以root用户访问NFS服务端时,被映射为root用户。以其他用户访问时同样映射为对应uid的用户,因为no_all_squash是默认选项 #sync 同步,同时将数据写入到内存与硬盘中,保证数据不丢失 #async 异步,优先将数据保存到内存,然后再写入磁盘,效率高,但可能丢失数据
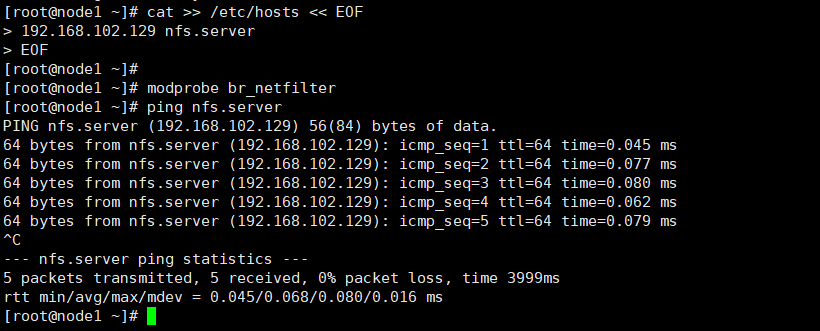
cat >> /etc/hosts << EOF 192.168.102.129 nfs.server EOF modprobe br_netfilter
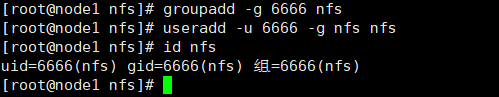
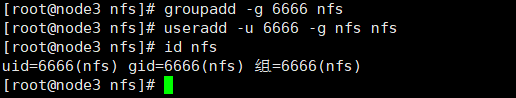
# 必须指定组id和用户id,而且服务端和客户端要一致,否则访客会变成nfsnobody groupadd -g 6666 nfs useradd -u 6666 -g nfs nfs id nfs vim /etc/idmapd.conf
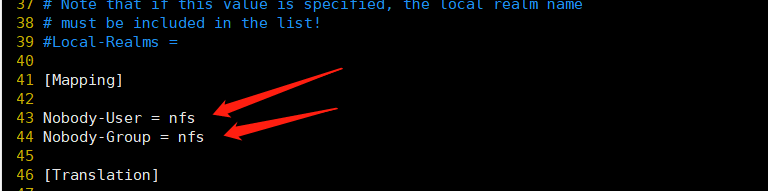
指定组和用户,注释Domain,改为刚才添加到hosts文件的域名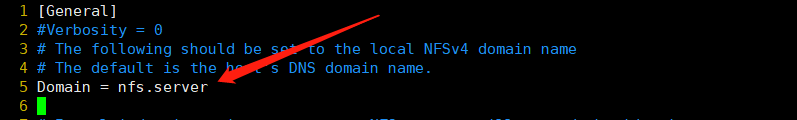
systemctl restart nfs-config systemctl restart nfs-idmap systemctl restart nfs-lock systemctl restart nfs-server systemctl restart rpcbind.service systemctl restart nfs.service service rpcidmapd restart
cd /data/nfs vim index.html cat index.html #刷新输出文件的列表 exportfs -rv
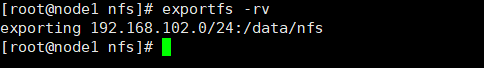
这里有个问题,那就是/data/nfs文件夹只有服务端的root用户有读写权限,这里我们给文件夹授权,这里配置了norootsquash:访客以root用户访问NFS服务端时,被映射为root用户。以其他用户访问时同样映射为对应uid的用户。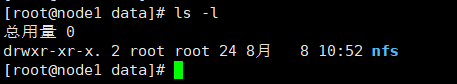
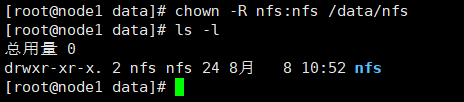
chown -R nfs:nfs /data/nfs ls -l
yum install rpcbind nfs-utils -y
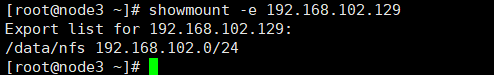
# 查看nfs服务器上共享输出了哪些文件夹 showmount -e 192.168.102.129
mkdir /data mkdir /data/nfs cd /data/nfs/ pwd
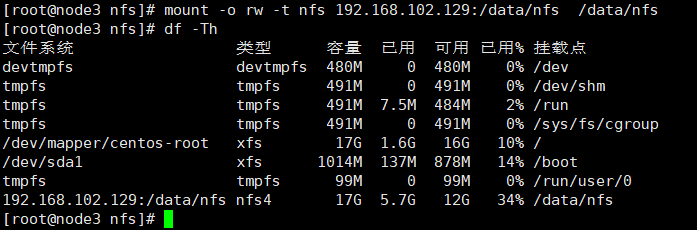
mount -o rw -t nfs 192.168.102.129:/data/nfs /data/nfs df -Th #取消挂载 umount -l /data/nfs
cat >> /etc/hosts << EOF 192.168.102.129 nfs.server EOF modprobe br_netfilter
# 必须指定组id和用户id,而且服务端和客户端要一致,否则会变成nfsnobody groupadd -g 6666 nfs useradd -u 6666 -g nfs nfs id nfs vim /etc/idmapd.conf
指定组和用户,注释Domain,改为刚才添加到hosts文件的域名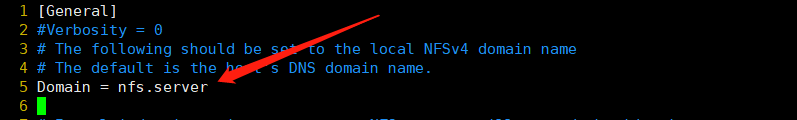
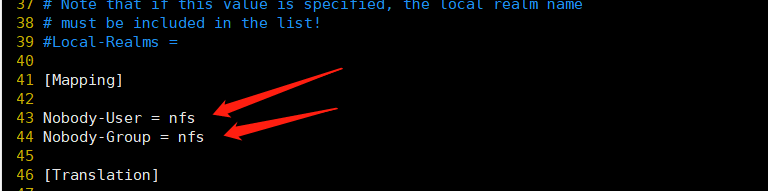
systemctl restart nfs-config systemctl restart nfs-idmap systemctl restart nfs-lock systemctl restart nfs-server systemctl restart rpcbind.service systemctl restart nfs.service service rpcidmapd restart
重新挂载文件
umount -l /data/nfs mount -o rw -t nfs 192.168.102.129:/data/nfs /data/nfs df -Th
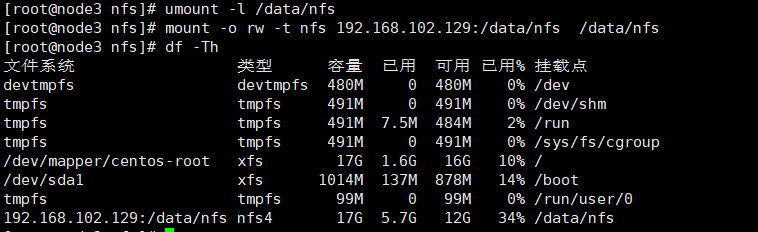
以root用户创建文件和文件夹
echo "test">>11.txt mkdir node02 ls -l
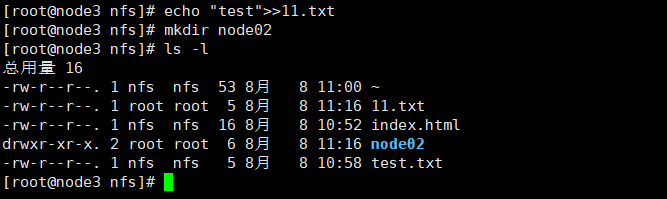
可以看到11.txt文件和node02文件夹的所属用户和组都是root
以 nfs 用户创建文件和文件夹
su nfs echo "test">>22.txt mkdir node03 ls -l
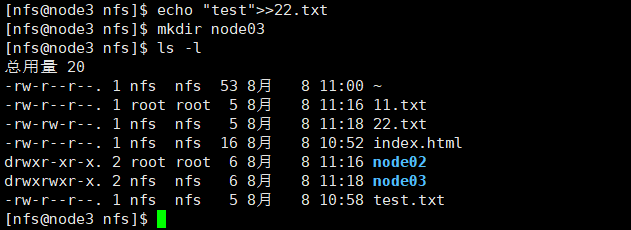
可以看到22.txt文件和node03文件夹的所属用户和组都是nfs